
Heat resistant conveyor belt
Heat resistant conveyor belts use high-temperature resistant special rubber, polyester canvas, or glass fiber as the skeleton layer, and are covered with heat-resistant rubber on the surface, and can withstand materials with a temperature of ≤800℃.
Temperature resistance: 200°C continuous, 400°C transient
Belt construction: EP fabric, 3-4 layers
Applicable environments: Steel, cement, power generation, smelting
What is a heat resistant conveyor belt?
Heat resistant conveyor belt typically consist of multiple layers: an outermost layer of heat-resistant cover rubber, a middle layer of high-temperature resistant reinforcing material (such as polyester canvas or steel wire rope), and a lower layer of heat-resistant rubber. These layers are bonded together using a high-temperature vulcanization process to form a unified structure, ensuring structural integrity and conveying functionality even under high temperatures.
-
When exposed to high temperatures, conventional conveyor belts rapidly age, crack, deform, and even burn, resulting in a sharp drop in tensile strength and a significantly shortened service life. This not only causes frequent downtime and production losses, but also poses serious safety risks. Heat resistant conveyor belt are crucial in these situations.heat resistant conveyor belt are designed for conveying high-temperature materials such as sintered ore, cement clinker, coke, steel slag, and fertilizers. They are typically made of polyester (EP), nylon (NN) canvas, or steel wire rope. Its heat-resistant temperature range covers extreme operating conditions from 100°C to over 600°C. It enables high-volume continuous conveying at rates ranging from 200 to 800 tons/hour.

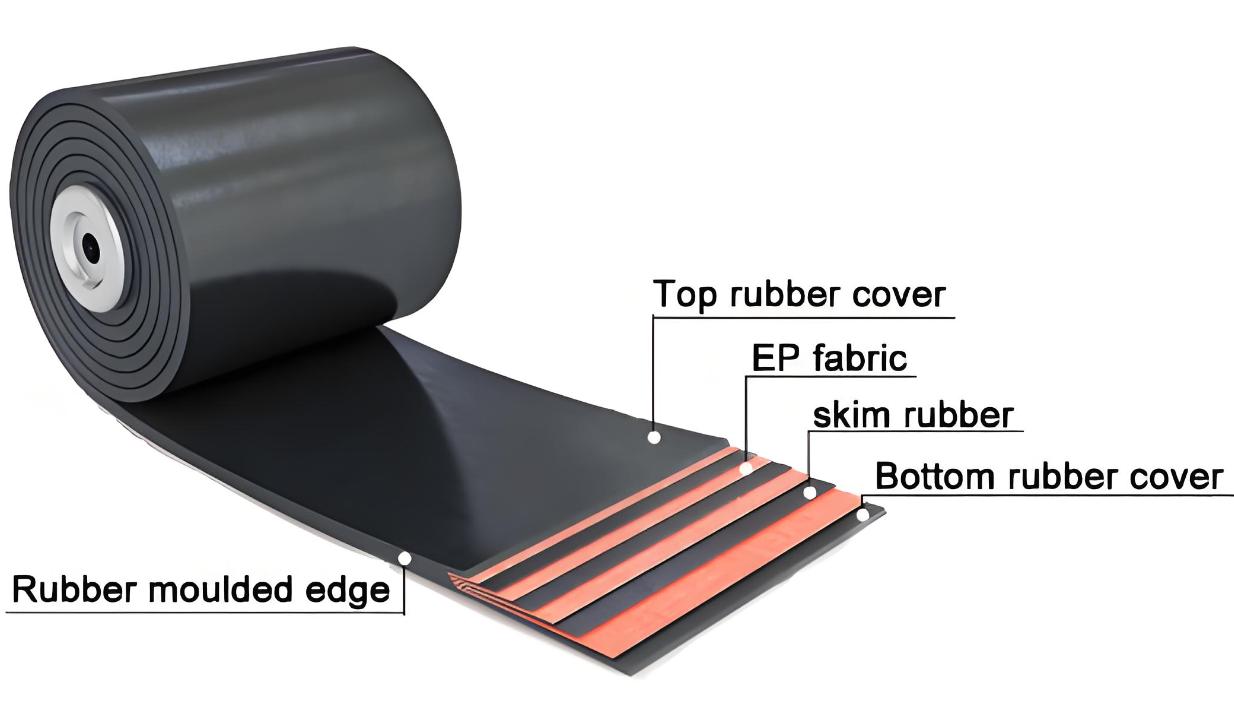
Heat resistant conveyor belt structure
The structure of a Heat resistant conveyor belt determines its high-temperature resistance and lifespan. Common belt widths range from 300 to 2200 mm, with thicknesses from 8 to 20 mm. The belt thickness can be selected based on material particle size, drop height, and wear. The main frame materials used are polyester (EP) and nylon (NN) canvas, which offer excellent strength and stability and are suitable for most medium- and high-temperature environments. For higher temperatures or longer conveying distances, a steel cord (ST) structure is often used, offering higher tensile strength and dimensional stability. However, careful attention must be paid to joint preparation and corrosion protection. High-quality heat-resistant belts often utilize multiple layers of heat-resistant canvas with insulating adhesive between the layers to prevent delamination or debonding caused by heat concentration.
Advantages of Heat resistant conveyor belt
Heat-resistant conveyor belts offer advantages such as high temperature resistance, aging resistance, wear resistance, long service life, and stable and reliable operation. The following is a detailed introduction to these advantages:
They can operate for extended periods in high-temperature environments, directly conveying hot materials such as sintered ore and cement clinker. This effectively prevents the belt from becoming brittle, hardening, or even melting due to high temperatures, ensuring continuous operation in core high-temperature processes in steel and cement industries.
Utilizing a composite structure of high-strength skeleton materials and special heat-resistant rubber, the conveyor belt not only withstands high temperatures but also possesses excellent wear resistance and tear resistance. Even when conveying sharp ores or experiencing high-drop impacts, it effectively resists tearing and abrasion, extending its service life.

Its special rubber compound formula ensures that the interlayer bonding strength does not decrease at high temperatures, preventing structural damage such as "delamination" during operation. Simultaneously, the anti-slip design of the working surface ensures sufficient friction between the belt and the drive roller, effectively preventing slippage and providing safety for high-speed, heavy-load conveyor lines.
Its excellent flexibility ensures smooth bending even on smaller diameter rollers, resulting in low running resistance. Furthermore, its high reliability significantly reduces unexpected downtime caused by belt damage, enabling continuous and stable material transport, thereby directly improving the overall conveying efficiency and capacity of the production line.
A single heat resistant conveyor belt can handle a variety of materials, from powdered cement and lime to lumpy ore, and even materials with certain corrosive or oily properties. This eliminates the need for frequent equipment changes due to differences in material temperature and properties, reducing operational complexity.

What are the three classifications of heat resistant conveyor belts?
Heat-resistant conveyor belts can be classified into three types based on their structure: edged heat-resistant conveyor belts, open heat-resistant conveyor belts, and inclined heat-resistant conveyor belts. The specific type can be selected based on the material being conveyed.
Edged Type:The conveyor belt surface has edges or vertical plates to prevent material slippage during conveying, suitable for inclined conveying. Common materials include high-temperature resistant PVC, heat-resistant rubber, silicone cloth, and aramid cloth. Conveying capacity is medium to large, affected by edge height and belt speed; belt width ranges from 300–2000 mm and can be customized; suitable for conveying bulk materials, granular or powdery materials in inclined or vertical directions.

Open Type:The conveyor belt is flat and without edges, suitable for horizontal or slightly inclined conveying of regular materials; common materials include heat-resistant rubber, fiberglass cloth, and silicone cloth; conveying capacity is small to medium, suitable for regularly shaped or large materials; belt width ranges from 300–1800 mm, selectable according to the size of the conveyed material.

Inclined type: The conveyor belt can be installed at an angle, usually used with sidewalls or corrugated edges to prevent material slippage; materials include high-temperature resistant PVC, heat-resistant rubber, and silicone cloth. Conveying capacity is medium, affected by belt width and inclination angle; belt width ranges from 400–1500 mm, adjusted according to the conveyed material and space layout; suitable for conveying materials from low to high or vice versa, saving space, and can be combined with sidewalls to prevent material slippage.

Heat resistant conveyor belt Specifications
| Standard Widths | Up to 2200mm (86") | Up to 5000mm (197") Available with longitudinal joint |
| Type Of Fabric | EP / NN / PP |
| Breaker Fabric Ply | Optional / as per customer requirement |
| Standard Belt Rating | 200 kN/m (110 PIW) to 3200 kN/m (1800 PIW) |
| No. of Ply's | 1 Ply to 8 Ply |
| Rubber Cover Thickness | 1mm (1/25") to 25mm (1") |
| Colour | Black |
| Edge | Cut Edge / Moulded Edge |
| Splicing Method | Hot / Cold / Mechanical |
| Single Roll Length | Standard Length : 300 meters (1000') | Up to 1000 meters (3300') depending upon total belt thickness |
| Standard Packing | Wrapping in HDPE sheets with Strapping. | (Wooden Crate / Metal Crate packing is available on request) |
| Belt Identification Number | A unique BIN (Belt identification number) at every 10 meters (33') |
Where are Heat resistant conveyor belt commonly used?
Heat resistant conveyor belt can be used for conveying hot materials in industries such as metallurgy, building materials, chemicals, and power generation, and can be flexibly integrated with other equipment. If the production process requires conveying at steep angles, it is recommended to choose a conveyor belt equipped with heat-resistant sidewalls and partitions to ensure excellent material loading and gradeability in high-temperature environments. For applications requiring long distances and high conveying volumes, heat-resistant steel cord conveyor belts can be selected to ensure stable operation. It can also be combined with vibrating feeders, bucket elevators, crushers, and screening equipment (such as vibrating screens) to form a complete high-temperature material handling system.

Temperature Range of Heat resistant conveyor belt
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) | Belt Surface Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Alloys | ||
| Stainless Steel | 900 - 1200 | 800 - 1000 |
| Inconel | 1000 - 1400 | 900 - 1200 |
| Tungsten | 1500 - 3400 | 1200 - 1500 |
| Molybdenum | 1200 - 2600 | 1100 - 1400 |
| Refractory Materials | ||
| Graphite | 2000 - 3000 | 1500 - 2000 |
| Silicon Carbide | 1400 - 1600 | 1200 - 1400 |
| Aluminum Oxide (Alumina) | 1400 - 1900 | 1200 - 1500 |
| Zirconium | 900 - 1500 | 800 - 1100 |
| Tantalum | 1400 - 3000 | 1300 - 1700 |
Heat resistant conveyor belt Manufacturer
Our factory boasts outstanding strength in Heat resistant conveyor belt manufacturing. Our extensive expertise allows us to optimize conveyor belt design from a systemic perspective. Our advanced production processes and strict quality control ensure consistency and high reliability in key processes such as belt core bonding and vulcanization. Our comprehensive product line covers various types of steel cord belts, from EP, NN, to ST, meeting varying temperature and strength requirements. We also provide professional selection guidance, joint technical support, and timely after-sales service to ensure optimal performance.





