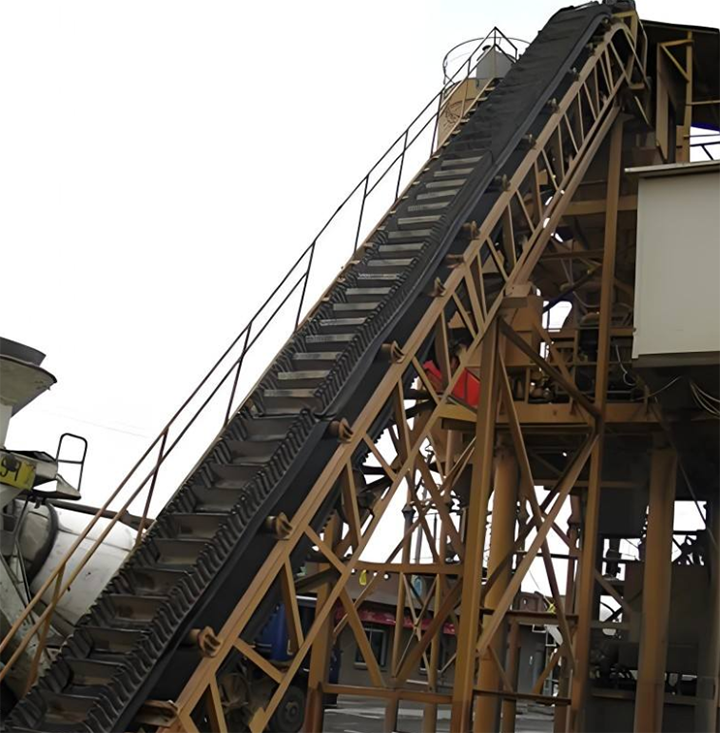
Industrial conveyor belts
Industrial conveyor belts, also known as conveyor belts, are products composed of a composite structure of rubber and fiber, metal and other fiber skeleton materials used in belt conveyors to carry and transport materials, or products composed of plastic and fabric composites.
Bandwidth (mm): Commonly 300, 500, 650, 800, 1000, 1200, etc.
Belt speed (m/s): Usually 0.8~2.5m/s, special customizable
Number of layers/skeleton material: such as EP cloth, NN cloth, wire rope, etc.
Thickness (mm): Select according to conveying requirements, such as 6mm, 8mm, 10mm, etc.
Industrial conveyor belts are devices used to efficiently move materials during production, manufacturing and logistics processes. They are widely used in a variety of industries such as mining, manufacturing, food processing, packaging, and airport baggage handling. Conveyor belt systems can be designed in many different configurations to suit specific tasks and environmental requirements.
Industrial conveyor belt systems primarily consist of core components such as a motor, drive rollers, idler rollers, load-bearing idlers, return idlers, tensioning devices, a circular conveyor belt, and a metal structural frame, all working in tandem. The system receives power from the motor, which is transmitted to the drive rollers via a reducer, using friction to drive the conveyor belt continuously. Key parameters such as operating speed and conveying capacity depend on the drive power; belt speed is typically 0.8-4.0 m/s, and belt width is 500-2400 mm. The conveyor belts are mostly made of materials such as rubber, PVC, and PU, possessing properties such as wear resistance, tear resistance, and, under specific operating conditions, high temperature resistance and antistatic properties.

What are the different types of industrial conveyor belts?
For conveying small batches of materials, light-duty conveyor belts can be selected, while for conveying large, abrasive materials, wear-resistant heavy-duty conveyor belts can be selected.
Light conveyor belts: Mainly use polymer materials, with an allowable working tension of less than 50N/mm, with thin belt body, good dimensional stability, high tension, bright colors, safe and non-toxic, etc., widely used in food processing, logistics transportation, tobacco production and other industries.

Fastener type: hook type and nail type, installed at both ends of the conveyor belt and connected by pins.
Thickness range: 0.5-8mm Typical bandwidth: 100-2000mm
Heavy conveyor belt: generally refers to rubber conveyor belt, using EP dipped canvas as the skeleton material, high strength, thin belt body, light weight, soft belt body, good troughing, good elasticity, and also has the characteristics of impact resistance, wear resistance and corrosion resistance. It is often used for heavy-load material transmission in metallurgy, building materials, mining, etc.

Fastener type: pin plate type and plate type. Pin plate type is suitable for small rollers, and plate type is suitable for larger rollers and applications that require no leakage splicing.
Thickness range: 8-30mm Typical bandwidth: 500-3000 mm
What is the working principle of industrial conveyor belts?
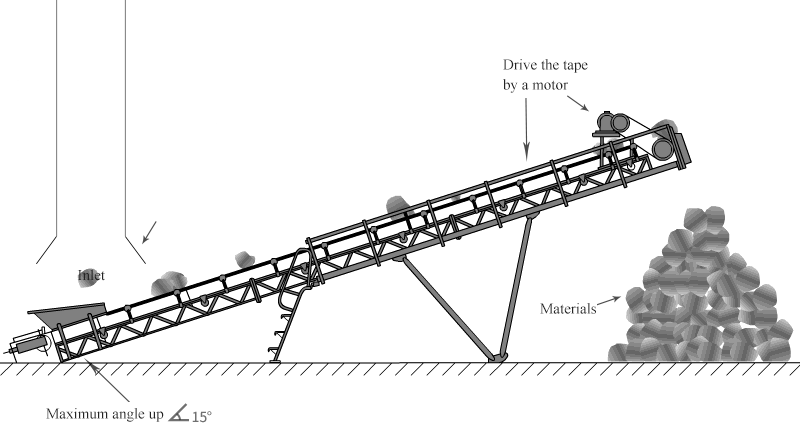
The conveyor belt is wound around the transmission roller and the tail roller to form an endless endless belt. The conveyor belt is supported by the support roller to limit the deflection sag, and the tensioning device provides the required tension for the normal operation of the conveyor belt. When working, the motor drives the transmission roller through the reducer, and the friction between the transmission roller and the conveyor belt makes the conveyor belt move continuously. The conveyed items are transported to the unloading location by the friction between it and the conveyor belt.
What are the structural components of industrial conveyor belts?
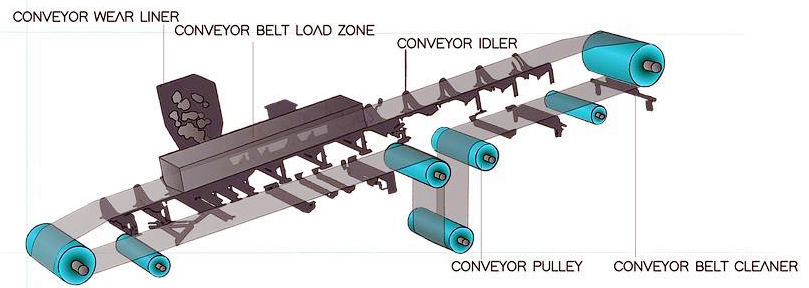
Generally consists of a covering layer, a skeleton layer and a bottom layer. The covering layer usually has the characteristics of wear resistance, oil resistance, acid and alkali resistance, etc., which is used to protect the skeleton layer and carry materials; the skeleton layer is the main supporting structure of the conveyor belt, providing strength and flexibility, and common materials include canvas, nylon, polyester, wire rope, etc.; the bottom layer is in contact with the driving roller and the roller, and is required to have good wear resistance and tear resistance.
Technical parameters of industrial conveyor belts
|
Category |
Model example |
Belt width (mm) |
Thickness (mm) |
Number of layers/skeleton material |
Features |
Applicable scenarios |
|
Light conveyor belt |
PVC-3.0MM-G |
300~2000 |
3.0 |
2-layer polyester cloth |
Anti-slip, green, food grade |
Food, electronics, logistics sorting |
|
PU-1.5MM-W |
200~1500 |
1.5 |
1-layer polyester cloth |
Food grade, oil resistant, cut resistant |
Pastry , meat processing line |
|
|
Modular plastic belt-MD50 |
Modular assembly |
≥300 |
- |
Removable, water-resistant, impact-resistant |
Aquatic products, refrigeration, filling line |
|
|
Teflon belt-TF260 |
100~1500 |
0.25~1.0 |
Glass fiber coated PTFE |
High temperature resistant, anti-sticking, breathable |
Heat sealing, baking line |
|
|
Heavy conveyor belt |
EP200-4800×6 |
400~2000 |
6~12 |
4 layers of EP cloth, 200N/ mm |
wear-resistant, high strength, impact resistance |
coal mines, building materials, cement plants |
|
NN300-51000×8 |
500~2200 |
8~16 |
5-layer NN cloth, 300N/mm |
high tensile strength, heat and humidity resistance |
fertilizer, ore, dock |
|
|
ST10001200×10 |
800~2400 |
10~20 |
wire core, 1000N/mm |
long distance, large load, high strength |
long line of mines and ports Transportation |
|
|
Heat-resistant HR-T41000×8 |
500~1800 |
8~14 |
EP cloth + high temperature resistant rubber |
Ablation resistance, crack resistance |
Cement kiln, coking line |
|
|
Pattern belt-Chevron |
400~1600 |
6~12 |
EP cloth + embossed rubber |
Non-slip, suitable for climbing |
Bulk material lifting, grain transportation |
What are the applications of conveyor belts in the industrial field?
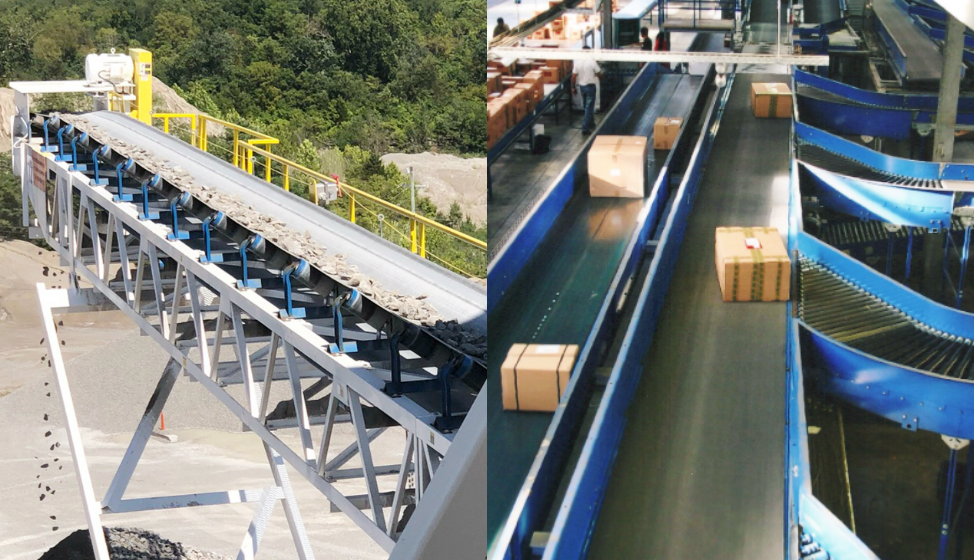

In automobile manufacturing workshops, industrial conveyor belts form the basic veins of automated production lines. Heavy parts such as engines and gearboxes are transported before assembly through heavy rubber conveyor belts and accurately positioned to assembly stations; lightweight materials such as interior parts and electronic components are sorted and transported by light PU conveyor belts to ensure a coherent and efficient production rhythm. In the electronics industry, precision chips, circuit boards and other products have extremely high requirements for cleanliness. Light anti-static PVC conveyor belts rely on their static-free and pollution-free characteristics to achieve material flow in dust-free workshops.

In the field of logistics and warehousing, conveyor belts are the key to achieving efficient sorting. In the express distribution center, modular chain conveyor belts and intelligent sorting systems can handle tens of thousands of packages per hour and automatically sort them to different exits according to the destination. In mining scenarios, long-distance, high-capacity steel rope core conveyor belts can continuously transport tons of ore from underground mining faces to surface processing areas. The maximum conveying distance can reach several kilometers, and the daily transportation volume can reach thousands of tons.
Industrial conveyor belts price
Standard PVC or lightweight PU conveyor belts typically cost between $10 and $50 per meter. However, rubber or silicone belts requiring high temperature resistance, abrasion resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, or food-grade standards can jump to $50 to $300 per meter. Sidewall conveyor belts, with the addition of sidewalls and partitions, are generally $100 to $400 per meter; the more complex the structure, the higher the price. Steel cord conveyor belts, used for heavy-duty long-distance transport in mines and ports, are the most expensive, reaching over $300 per meter. The price depends on the number of canvas layers, cover rubber thickness, tensile strength, steel cord diameter, and rubber grade.

What is the general carrying capacity of belt conveyors?
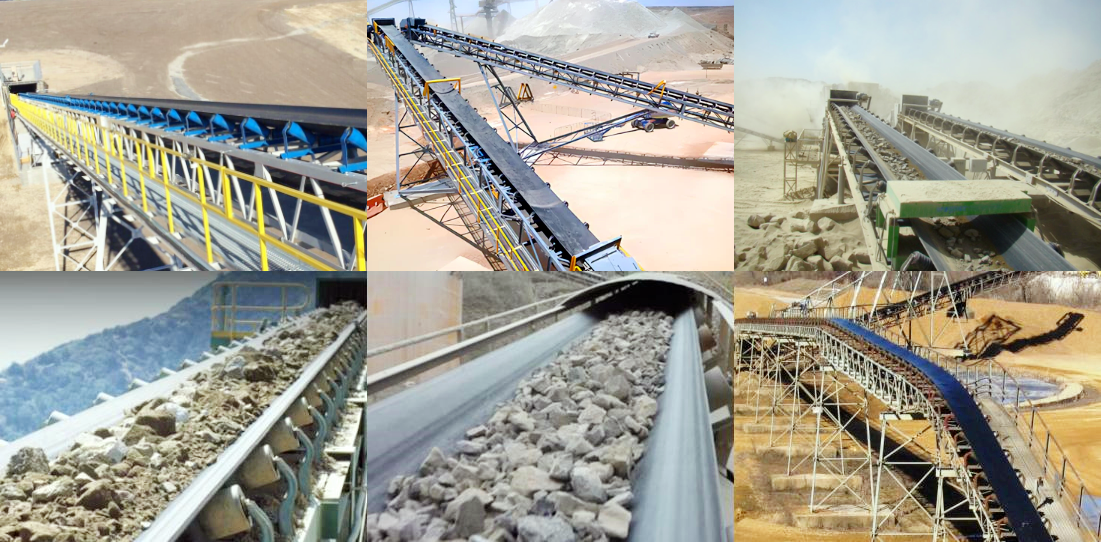

The carrying capacity of belt conveyors varies depending on the design, purpose and working environment. Generally speaking, its carrying capacity can range from light load to heavy load:
Light load conveyor: Commonly used in light industrial fields such as food and electronics, the weight of a single conveyed material is usually between 10 and 200 kilograms.
Medium load conveyor: Widely used in scenes such as industrial assembly lines, the weight of materials that can be carried is generally between 200 and 500 kilograms.
Heavy load conveyor: Mainly used in mines, ports and other occasions where bulk materials need to be handled, and the weight of a single conveyor can reach more than 1 ton. Some specially designed heavy-duty conveyors can even carry tens of tons to meet the needs of extreme industrial environments.
The following are the theoretical load capacity ranges under some common specifications (horizontal conveying, uniform loading):
|
Bandwidth (mm) |
Conveying speed (m/s) |
Conveying capacity (t/h, estimated based on a bulk density of 1.0t/m³) |
|
500 |
1.0 |
100~150 |
|
650 |
1.25 |
150~300 |
|
800 |
1.6 |
300~500 |
|
1000 |
2.0 |
500~800 |
|
1200 |
2.5 |
800~1200 |
|
1400 |
3.15 |
1000~1800 |
Industrial conveyor belt supplier
Dahan Machinery provides a variety of industrial conveyor belts and conveying systems, covering light and heavy applications, suitable for mining, construction, ports, agriculture, food processing, chemicals, waste treatment and other industries. Its products are known for their high efficiency, durability and customization, meeting various material conveying needs.
Light conveyor: The load capacity is generally 50-100 kg/m², and the conveying volume is 10-200 t/h, which is suitable for short distance and low load scenarios.
Heavy conveyor: The load capacity is 500-5000 kg/m², and the conveying volume can reach 30-3000 t/h, which is suitable for long distance and high load applications.





