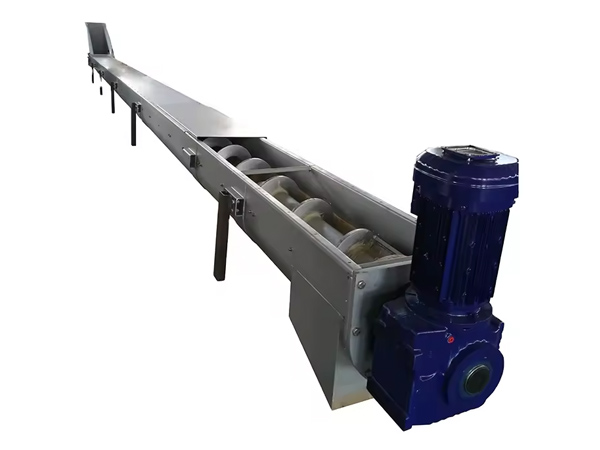
Steel Screw Blade Inside
Wednesday June-04 2025 16:06:45
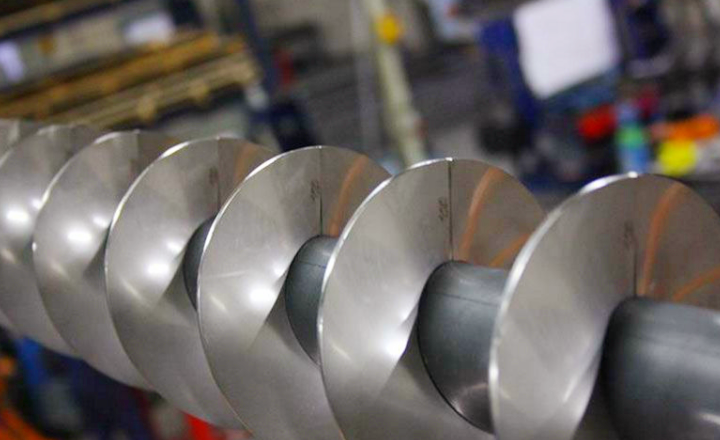

Core functions of steel screw blade inside
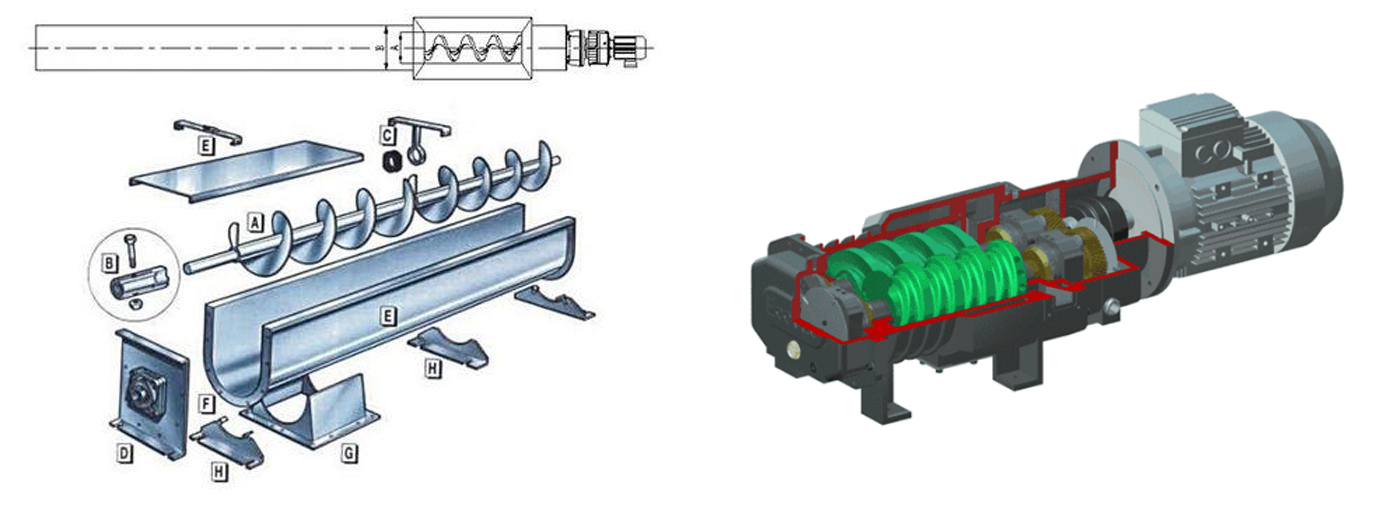
Conveying/propulsion: When the blades rotate in a pipe or trough, their spiral shape generates axial thrust, pushing the material (powder, granules, slurry, or even lumps) from the inlet to the outlet.
Mixing/stirring: The rotation of the blades can effectively stir, flip and mix the materials of different components in the trough.
Compression/extrusion: In some designs (such as the end of the screw conveyor), the change in the blade spacing or pitch can exert pressure on the material to achieve compression or extrusion molding.
Feeding/metering: By controlling the speed of the blades, the amount of material conveyed can be accurately controlled to achieve quantitative feeding.
What are the types of steel screw blade insides?

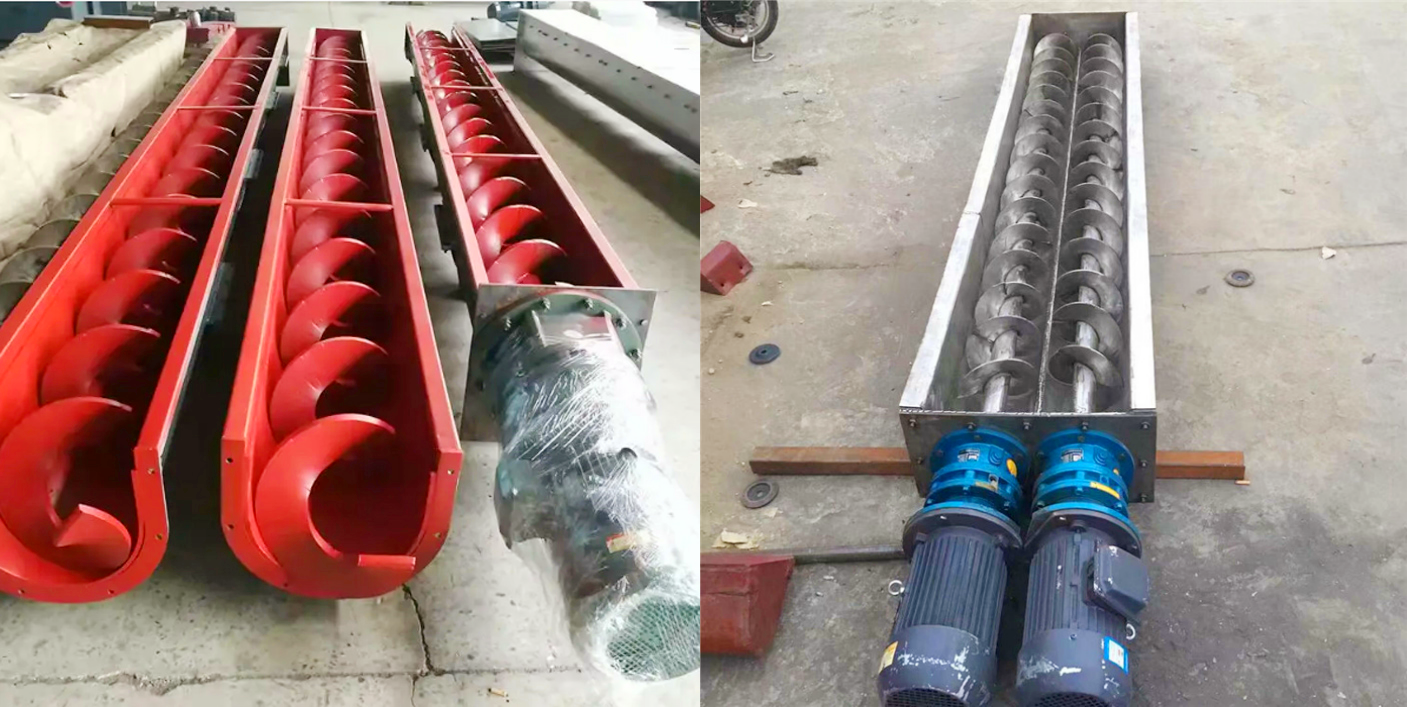
A shafted spiral blade is a spiral blade mounted on a central shaft. This central shaft is usually a solid or hollow metal rod that supports the spiral blade and transmits the rotational power. Due to the existence of the central shaft, the entire screw conveyor structure is more solid and can withstand greater loads. It is suitable for the conveying of most materials, especially bulk, granular or small block materials, and is particularly suitable for those occasions that require high equipment strength and stability.
The shaftless spiral blade has no central axis, but is a tubular structure directly composed of spiral blades. The shape is maintained by setting one or more support rings on the outside of the blade, and the spiral blade is driven to rotate by an external drive device. Without the obstruction of the central axis, the shaftless screw conveyor can work in a more compact space and can handle some more viscous or easily entangled materials. For conveying belt-shaped, fibrous or easily entangled materials (such as domestic garbage, pulp, etc.), the shaftless design can effectively avoid the blockage problem caused by the material entangled on the shaft. It is mainly used to handle materials with special properties, such as sludge, domestic garbage and other materials that are easy to entangle and difficult to handle.
Differences between stainless steel and carbon steel screw blade inside

|
Comparison items |
stainless screw blade inside |
carbon steel screw blade inside |
|
Main materials |
austenitic stainless steels such as 304 and 316L |
ordinary carbon structural steels such as Q235, Q345, and 16Mn |
|
Corrosion resistance |
extremely strong, suitable for acidic or humid environments |
poor, easily corroded, and requires anti-corrosion coating |
|
Wear resistance |
general, moderate |
good, optional thickness or wear-resistant treatment to enhance performance |
|
Strength performance |
moderate strength, not easy to deform |
high strength, strong rigidity, good bearing capacity |
|
Cleaning performance |
smooth surface, not easy to hang, easy to clean |
relatively rough surface, hanging phenomenon is more obvious |
|
Applicable materials |
food, chemical, pharmaceutical, corrosive materials |
cement, coal powder, sand, stone, building materials and other conventional materials |
|
Common uses |
food grade conveyors, chemical powders, pharmaceutical raw materials, etc. |
building materials transportation, ore transportation, industrial waste treatment, etc. |
How to choose steel screw blade inside
When choosing steel screw blade inside, the key is to match material characteristics and blade types.

First, consider the fluidity of the material: for free-flowing materials such as grains and powders, continuous blades or segmented blades in shafted spiral blades are usually efficient and economical choices. However, if the material is highly viscous and easy to entangle (such as sludge and fiber), shaftless spiral blades can better avoid blockage and ensure smooth transportation.
The second is the corrosiveness or hygiene requirements of the material: stainless steel spiral blades are ideal for industries such as food, medicine, chemicals, and sewage treatment due to their excellent corrosion resistance and easy cleaning; while for non-corrosive and dry general industrial bulk materials, carbon steel spiral blades are an economical choice due to their low cost, but attention should be paid to rust prevention.
In addition, the abrasiveness of the material, the conveying volume, and whether special functions such as mixing and crushing are required should also be considered. These will further refine the design of the shafted blades, such as the use of wear-resistant steel, variable pitch, belt or paddle types, and ultimately ensure that the selection takes into account both performance and cost.
Price of steel screw blade inside

Shaftless spiral blades are usually more expensive than shafted ones because they require thicker materials and special manufacturing processes to ensure strength, and usually also require matching linings.
Carbon steel blades: usually range from tens to hundreds of S$ per meter, depending on size, thickness, presence or absence of shaft, etc. A single small diameter, standard design blade may start from tens of S$.
Stainless steel blades: The price is usually 1.5 to 3 times or even higher than carbon steel, and large, complex or high hygiene stainless steel blades may reach hundreds to thousands of S$ per meter.
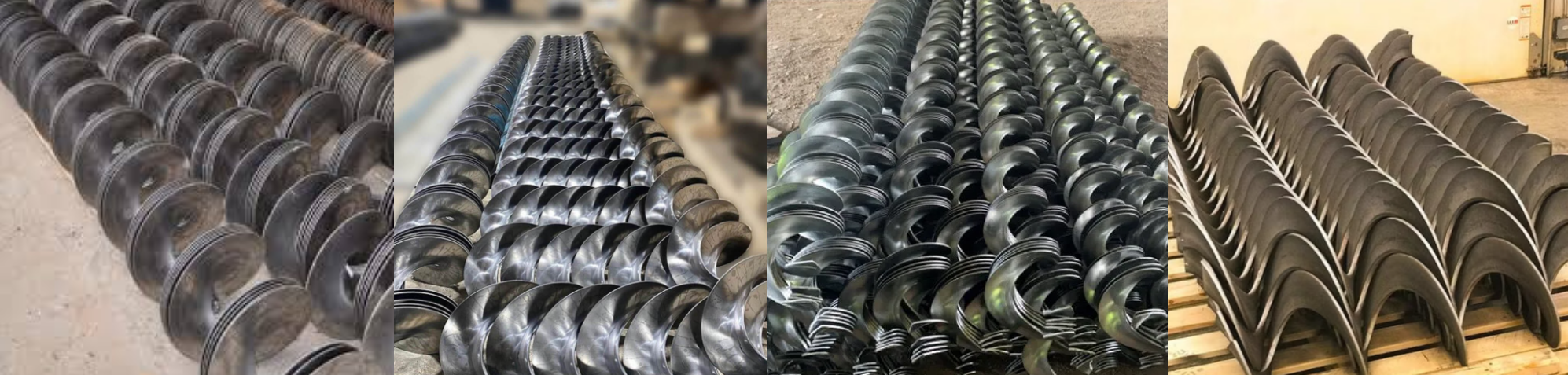

Steel screw blade insides are an extremely versatile industrial component. Its core value lies in utilizing the strength and wear resistance of steel to achieve efficient material conveying, mixing, compression and other functions through spiral rotation. The design needs to be closely combined with material characteristics, process requirements and environmental conditions. It is an indispensable key component in many fields such as bulk material handling. If you have a specific application scenario, encounter problems (such as fast wear, blockage, low efficiency) or need selection advice, provide more details and I can give more targeted information.